Speaker
Description
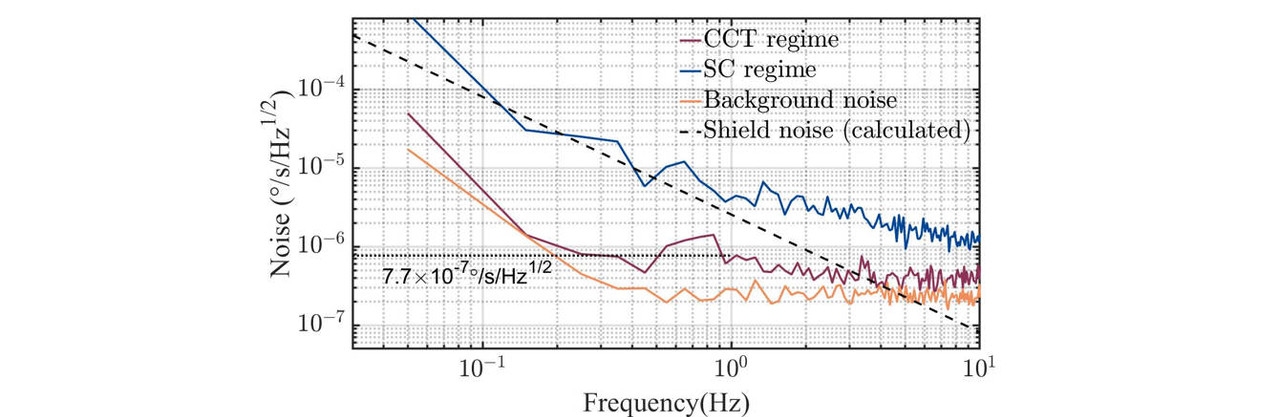
Comagnetometers have enabled significant progress in searches for physics beyond the standard model and inertial navigation, owing to the ability to substantially suppress magnetic noise. We present a novel type of comagnetometer based on the cooperative coherence transfer (CCT) mechanism [Submitted]. The nonreciprocal coupling is introduced to enable optimized transfer energy matching and improve the transfer efficiency. We demonstrate this mechanism in a $^{21}$Ne-Rb-K comagnetometer, yielding a 15-fold enhancement of the magnetic noise suppression effect compared to the conventional self-compensation (SC) regime [Phys. Rev. Lett. 89. 253002 (2002)]. Consequently, an ultrahigh sensitivity of $7.7\times 10^{-7~\circ}/\text{s}/\sqrt{\text{Hz}}$ from 0.2 to 1.0 Hz, equivalent to $8.7\times10^{-24}~\text{eV} /\sqrt{\text{Hz}}$, is achieved, demonstrating the highest energy resolution [Quantum Sci. Technol. 7. 014001 (2022)]. This platform facilitates potential improvements of over 4 orders of magnitude in constraints on dipole-dipole interaction and monopole-dipole interaction, with broad application prospects.