Speaker
Description
Introduction
The estimation of dose errors is a key part of online adaptive particle therapy. Interplay distorts dose distributions leading to non-ideal tumor coverage and higher dose to healthy tissues.
Fast forward dose calculation (FDC) is mandatory to verify the efficacy of motion mitigation strategies during treatment. We propose and validate in silico a system to reconstruct the planned and delivered RBE-weighted 4D-dose in real-time, i.e. within each accelerator cycle (<5 s) of the carbon ion therapy delivery.
Material and Methods
The GPU-based FDC algorithm was based on the existing RIDOS dose calculation tool.
For real-time delivered dose calculation, the fast FDC was interfaced with the research version of the CNAO Dose Delivery System (DDS) through a TCP/IP connection, providing measured and planned spot properties (MU, beam position and motion phase) during the delivery. The algorithm evaluates the cumulative delivered and prescribed dose distributions in parallel to delivery and performs a gamma-analysis comparison at the end of each slice. The results are updated on a graphical user interface (Fig. 1).
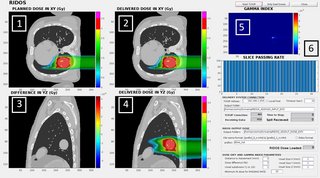
The system has been tested in silico on a virtual XCAT 4DCT, with a simulated data stream from the DDS for dose reconstruction. For verification of advanced motion mitigation strategies, we designed RIDOS to be compatible with the recently developed MultiPhase 4D delivery (MP4D).
Results
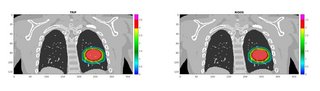
The framework successfully performed the FDC of each simulated spill before the end of the accelerator cycle. The overall computation time per spot was ~0.45 ms. The reconstructed dose was validated against the research treatment planning system TRiP (Fig. 2), showing good agreement with gamma-index passing rate (3mm/3%)>98%.
Conclusions
We demonstrated the feasibility of a real-time dose calculation with clinically acceptable precision.
The next step will involve experimental tests with carbon and proton beams at the CNAO facility, as well as consideration of more patient data, with variable motion and motion mitigation strategy. In the future, this framework will open the door for possible real-time adaptive particle therapy.
Funded by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 955956
